لاگرینج ضارب
(Lagrange multipliers سے رجوع مکرر)
ریاضیاتی کاملیت میں، طریقۂ لاگرینج ضارب (جو لاگرینج کے نام پر بولا جاتا ہے) کسی دالہ جو بندشوں کے زیر ہو کے عظمٰات اور صغیرات ڈھونڈنے کی ایک حکمت عملی فراہم کرتا ہے۔

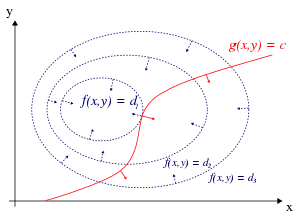
مثال کے طور پر (بائیں طرف شکل 1 دیکھو) کاملیت مسئلہ کو برتو، جس میں فنکشن کی تکبیر کرنا ہے جبکہ بندش کی بھی تسکین ہوتی ہو، یعنی
- maximize
- subject to
اب ہم نیا متغیر () متعارف کراتے ہیں، جسے لاگرینج ضارب کہتے ہیں اور اس لاگرینج فنکشن کا مطالعہ کرتے ہیں جو یوں تعریف ہے:
اگر نقطہ اعظمی ہو اصل بندشی مسئلہ کا، تو پھر ایسا λ وجود رکھتا ہو گا کہ نقطہ لاگرینج فنکشن Λ کا ساکن نقطہ ہو (ساکن نقاط وہ نقاط ہیں جہاں Λ کا جزوی مشتق صفر ہوں)۔ البتہ، تمام ساکن نقاط اصل مسئلہ کا حل نہیں دیتے۔ اس لیے، طریقۂ لاگرینج ضارب بندشی مسائل میں کاملیت کی لازم شرط ہے۔[1][2][3][4][5]
- ↑ Dimitri P. Bertsekas (1999)۔ Nonlinear Programming (Second ایڈیشن)۔ Cambridge, MA.: Athena Scientific۔ ISBN 1-886529-00-0
- ↑ سانچہ:Springer.
- ↑
- Leon S. Lasdon (1970)۔ Optimization theory for large systems۔ Macmillan series in operations research۔ New York: The Macmillan Company۔ صفحہ: xi+523۔ سانچہ:MR
- Leon S. Lasdon (2002)۔ Optimization theory for large systems (reprint of the 1970 Macmillan ایڈیشن)۔ Mineola, New York: Dover Publications, Inc.۔ صفحہ: xiii+523۔ سانچہ:MR
- ↑ Jean-Baptiste Hiriart-Urruty، Claude Lemaréchal (1993)۔ "XII Abstract duality for practitioners"۔ Convex analysis and minimization algorithms, Volume II: Advanced theory and bundle methods۔ Grundlehren der Mathematischen Wissenschaften [Fundamental Principles of Mathematical Sciences]۔ 306۔ Berlin: Springer-Verlag۔ صفحہ: 136–193 (and Bibliographical comments on pp. 334–335)۔ ISBN 3-540-56852-2 النص "سانچہ:MR" تم تجاهله (معاونت)
- ↑ Claude Lemaréchal (2001)۔ "Lagrangian relaxation"۔ $1 میں Michael Jünger and Denis Naddef۔ Computational combinatorial optimization: Papers from the Spring School held in Schloß Dagstuhl, May 15–19, 2000۔ Lecture Notes in Computer Science۔ 2241۔ Berlin: Springer-Verlag۔ صفحہ: 112–156۔ ISBN 3-540-42877-1۔ doi:10.1007/3-540-45586-8_4۔ سانچہ:MR.doi:10.1007/3-540-45586-8_4







